Difference between ALE and EDI ?
ALE is used to support distributed yet integrated processes across several SAP systems whereas EDI is used for the exchange of business documents between the systems of business partners (could be non-SAP systems)
ALE is SAP's technology for supporting a distributed environment whereas EDI is a process used for exchange of business documents which now have been given a standard format
Both ALE and EDI require data exchange. An Idoc is a data container which is used for data exchange by both EDI and ALE processes.
The interface concept of classical RFC system is based on basically two different strategies : RFC and data exchange through Idoc Message Documents.
RFC makes direct and Synchronous calls of a program in a remote system.
BAPIs are a subset of RFC enabled functions modules in R/3 especially designed as API to the SAP object, or in other words : Function module officially released by SAP to be called from external world.
What is an Idoc? Idocs are text encoded documents with a rigid structure that are used to exchange data between R/3 system and a foreign system. instead of calling a function in destination system data is fist packed into an Idoc and then sent to the receiving system, where it is analyzed and properly processed.
Therefore an Idoc transfer is always an asynchronous system. The significant difference between RFC and Idocs is that every action in Idocs is protocolled by R/3 and Idocs can be reprocessed in case of any error in one of the message steps.
What is ALE and IDOC and EDI ? While Idocs have to understood as a data exchange protocol, EDI and ALE are typical use cases for Idocs. R/3 uses Idocs for both ALE and EDI to deliver data to the receiving system,
ALE is basically a scheduling mechanism that defines when and between which partners and what kind of data will be exchanged on a regular or event triggered basis. such a set up called ALE scenario.
EDI If we send data to an external partner, we generally speak of EDI, while ALE is a mechanism to reliable replicate data between trusting systems to store a redundant copy of the IDoc data.
when there is a conversion of data say a Purchase Order from your system to a sales order in the later system, then we use Idocs (or EDI). But when we wanted to send a Purchase order which is to be the same in the later system then we use ALE or BAPI.
The main difference between EDI and ALE, BAPI is in the transfer of data. For EDI the transfer of data is from IDoc's( Intermediate documents) to a flat file. Where as in ALE and BAPI it is from Memory to memory transfer.
Difference Between ALE and EDI :Normally we refer to EDI technology when a non SAP system is one of the communication channel. ALE communication occurs from the SAP side and EDI from the non-SAP side. IDOCs uses ALE and EDI to deliver the data to the receiving system. If the data needs to be exchanged between two SAP systems, then IDOC uses ALE technology . For the exchange of data between a SAP and Non SAP system, IDOC uses EDI subsystem to convert and deliver the data.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What is EDI :
- EDI is electronic exchange of business documents between the computer systems of business partner using a standard format over a communication network.
EDI is also called paperless communication.
Typical EDI/IDOC Scenario:
1) Some ABAP transaction writes data in R/3 tables.
2) An external application request for this data.
3) An Idoc handler creates the Idoc and converts data to ASCII format.
4) An external program converts to international standards.
5) data is sent to the receiver via ftp, isdn etc.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SAP ABAP YOU-TUBE :
Manufacturer ----Idoc--------> Distributor -------Idoc------> Sellers
Control Record/ data : EDIDC
DATA Record : EDIDD (structure) EDIDD_OLD (store data)
Status Record : EDIDS
Transactions:
- WE02 or WE05 : transaction for IDOC reporting in SAP ABAP, weather the IDOC is came to SAP or all the details about an IODC statuses.
- How Idoc looks like :
- Data Record and status Record: data send in Idoc is form of small segments.
process: Normally an middle ware converts SAP Idoc to XML format and send to the receiver target system.
IDOC_XML_DISPLAY : to display XML for an IDOC. IDOC also store data in hierarchical order as does the XML. so it is easy to have IDOC into XML format.
Why We need Idoc when we have BAPI , RFC :
- To do not have control in non SAP system every time.
- mapping not required in Idoc although it is in BAPI.
- Idoc has a unified structure for data transmission.
GENERAL INFORMATION FOR COMMON IDOC MESSAGE TYPES
IDOC TERMINOLOGIES:
==========================================
- IDOC (BASIC) Types (table EDBAS): (WE30)
- Basic Types or Idoc Type defines the structure of IDOC. It contains data in other words.
- It contains exact structure in which sequence data transferred form one system to other,
- Each basic type describes standard Idoc segments, format of data fields and their size.
- Basic type also defines number of segments and fields in an Idoc.
- All the fields which are necessary for transmission of message for a particular business transaction are mapped in different segments.
- It also defines the structure and relationship of Idoc segments along with mandatory and optional segments.
- IDOC Extension :
- Basic types contains all the standard fields that are necessary for carrying out a necessary transaction. However if any additional fields need to be sent to the partner we can make use of the Idoc Extension feature.
- Idoc extension is extension of basic type and contains additional custom Idoc segements ad fields that are not available in the standard Idoc type.
- Idoc Segments:
- Idoc segments are actually contains data that needs to be send or receive from partner.
- These segments contains the actual values that are sent as a part of transmission.
- Parent and Child Segment:
- Idoc Segments are called parent if it contains its own segment, and the dependent segment called the child segment.
- Inbound and Outbound Idoc:
- Idoc Directions:
- If the information is sent outside the system then the direction is outbox (1) and when it is received into the system then direction is inbox (2).
- PARTNER:
- Partner is the business partner with which the exchange of data through Idoc is placed. it can be vendor, customer or any other system.
- Depending on the direction of information in which the information is sent it plays the role of either sending partner or receiving partner.
- Partner Type:
- used to identify partners within the SAP system.
- Partner type is KU for customer, LI for VENDOR and LS for logical system.
- Message Type : (Table EDMSG) (TCODE WE82/WE81)
- For which purpose Idoc going to fire.
- Idoc Processing involves transmission or receipt of document in form of a message, each of which represents a document in SAP.
- These documents can be Order, Shipment Confirmation, Advance shipping Notification, goods receipt, or invoice.
- Message Type is associated with the Basic Idoc Type and defines kind of data or the document that is exchanging within the partner.
IDOC type defines the structure and format of the data that is being exchanged Message Type determines and process the various Outputs associated with an Application doc.
- PROCESS CODE: (WE41 & TEDE1 (Outbound) and WE42 & TEDE2 (Inbound) to display process code details)
- The process code contains details of the function module that are used for the Idoc Processing. Process code can be linked to the Message type.
- Process Codes are used in both ALE and EDI framework to identify the corresponding program :
- OUTBOUND : Process code acts as Selection programsINBOUND : Process code acts as function modules.
- Process Code is linked to the Function Module in SAP that converts application data into an IDoc. Standard function modules are provided by SAP for this conversion however these can also be customized as per business needs.
- PORT :
- IDOC port contains information about the way data is sent between the source and the target system.
- The type of port defines the information contained within the port.
- For example:
- Port Type Internet : contain IP address of the target system.
- Port Type file : contains directory or file name information is maintained.
- Port Type 'tRFC' : conatins the information about RFC destination of the target system.
- For Idoc transmission using ALE 'tRFC' Port are used.
- PARTNER PROFILE MAINTENANCE (WE20) :
- Partner Profile must be maintained for all the business partners to whom we want to send or receive Idocs.
- Partner profiles contain parameters for inbound and outbound processing of Idocs.
- For each message type we can maintain inbound/outbound options, message control, post processing options and contact information within inbound and outbound parameters.
- Outbound Options (Outbound Parameters):
- This involves sender/receiver port, Output mode and relation to Idoc type, i.e. Basic Idoc Type and Extension.
- Message Control (Outbound Parameters):
- This contains :
- application for which IDoc will be created e.g. 'V3' = 'Billing' in Sales and Distribution (SD).
- The message type of the application that will trigger the Idoc and
- the process Code that will convert SAP Document to an Idoc.3
- For example, if PO is to be sent to the Vendor 3018, then in the outbound option of the partner 3018 we need to maintain the message type LPH1 and link it to the Process Code ME14. So when message type LPH1 is triggered in the PO then an IDoc will be created for the partner vendor 3018.
- Change Message Indicator :
- This indicates whether the Idoc is sent as a notification of change.
- For Example : Purchase order change messages are sent to vendor using EDI standard message type 860. separate message type should be triggered in the purchase order for PO change. and an additional line must be added in message control tab with change management indicator on.
- Inbound Options ( Inbound Parameters) :
- For inbound options process code maintained in the inbound parameters only.
- Idoc processing can be triggered by background program or immediately.
- POST PROCESSING (Inbound/Outbound Parameters):
- In this option we have name or position (workflow details) of teh users or positions to which an error notification will be sent if an Idoc Processing fails.
===========================================================
IDOC STRUCTURE AND RECORDS
- Structure :
- Divided into control record and data record and status record.
- These records are stored in transparent tables of SAP , these tables are EDIDC , EDID4, EDIDS.
- Control record (EDIDC) :
- It contains information such as :
- Idoc Number
- Direction (Inbound or outbound)
- Status of Idoc
- Basic Type
- Message Type
- Partner (sSender/Reciever) (Port, Partner number, Partner Type)
- Tiem Dat eopf creation of Idoc
- Data Record (EDID4) :
- It contains the details of Idoc segments.
- Idoc segment has fields that contain the data necessary for posting the documents.
- Status Record (EDIDS):
- Idoc status defines different processing status of the Idoc.
- Idoc statuses are used to track the IDoc and its various States.
- Different status numbers represent the Idoc status.
- current status of teh Idoc present in control record.
- Initial status number of Idoc is
- 64 for inbound and
- 01 or 30 for outbound.
- successful status number is
- 53 for inbound and
- 16 for outbound Idocs.
SENDING AND RECEIVING IDOCS
- Triggering an outbound IDoc :
- Can be triggered from the output message types of purchase orders, deliveries, invoices, Material Documents etc.
- here are the different statuses of the outbound Idoc:
- 01: IDoc generation successful
- 30: IDoc is ready to be processed by IDoc Processing job
- 03: IDoc data is passed to the Port
- 18: IDoc successfully triggered EDI subsystem
- 06: IDoc data translated to EDI format
- 12: IDoc is dispatched successfully to the partner
- 16: Partner has received the IDoc successfully
- Receiving an inbound Idoc:
- The initial status of an inbound IDoc is 64 and successful status is 53.
- Different validation steps for inbound IDocs are explained below:
- 50: IDoc received successfully in the system
- 64: IDoc is ready to be processed by IDoc processing job
- 53: Application document created and saved successfully. The document number can be found by expanding the status node 53
IDOC PROCESSING
- AUTOMATIC/IMMEDIATE PROCESSING
- In this case, IDoc are processed immediately as they generated or added in the system. The check “Transfer IDoc immediately” is selected in Outbound Options and “Trigger Immediately” is selected in Inbound Option. These checks are generally used when the real time information exchange is necessary between two systems.
- Manual Processing
- IDocs can also be manually processed using the TCODE BD87 in SAP.
- PROCESSING VIA BACKGROUND JOB
- IDoc processing by background is the most preferred way of processing the IDocs. Following Programs are used from processing the IDocs using background job:
- Report RBDAPP01 : Inbound IDocs
- Report RSEOUT00 : Outbound IDocs
- Processing IDocs:
Testing and Editing Idocs
- When an IDoc is edited the original IDoc information(backup) is saved in a New IDoc under status 70 (for inbound) / 33 (for outbound).
- These IDoc stays in the system for reference only and cannot be processed.
- The status of the edited IDoc becomes 69 (inbound) and 32 (outbound).
- Debugging of IDocs can be done using by copying the IDocs using TCode WE19.
- The newly generated IDoc can also be processed using BD87.
Changing Idoc status
- Report RC1_IDOC_SET_STATUS can be used to change the status of IDoc. Status changes are generally needed to move an IDoc to status 68 – no further processing.
- Normally not allowed for all. (for Internal EHS Use Only)
- TCODE WE09: SEARCHING DATA IN IDOC SEGMENTS
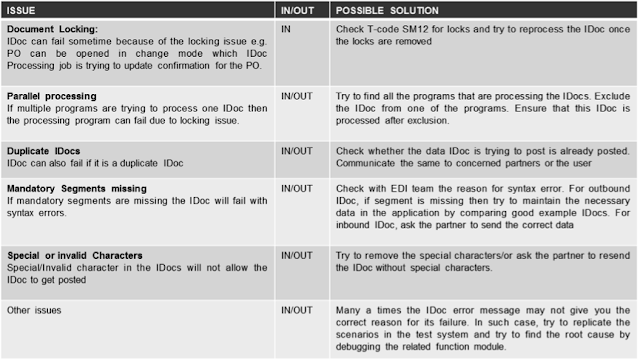
IDOC VALIDATIONS, COMMON IDOC ERRORS AND SOLUTION
- Though, the IDoc failure may not be related to any of the above mentioned reasons, the best way to find the IDoc error is to compare the existing IDoc with the good example. Good example IDoc can be easily searched with any of the IDoc search methods as described above.
DOCUMENTATION FOR IDOC TYPES
IDoc documentation can be found using TCODE WE60 and can be helpful to obtain information of the IDoc Type or its particular segment. It also provides information such as mandatory and optional segments, minimum and maximum number of segments, etc.
Archiving Tcode SARI (Archiving explorer).
Important Transaction:
Important Transaction:
- WE20 : Partner profiles
- WE21 : Port in ABAP
- WE09 : searching data in Idoc segment














I can set up my new idea from this post. It gives in depth information. Thanks for this valuable information for all,..
ReplyDeleteBitcoin to Neteller